Proxy Pattern
Proxy Pattern
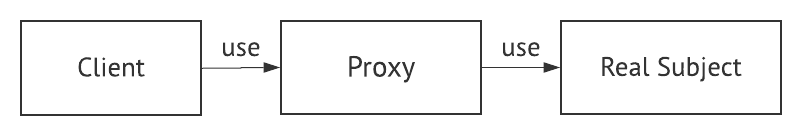
Proxy Class를 통해 대신 전달 하는 형태로 설계되며, 실제 Client는 접근하려는 객체(Real Subject)를 바로 접근하는게 아닌 Proxy로 부터 결과를 받는다.
Proxy: 대리인 이라는 뜻, 뭔가를 대신하여 처리하는것
주로 logging, 혹은 부가적인 기능을 추가할 때 사용한다. DataJPA Repository, Hibernate Entity 등… 다양한 곳에서 사용한다.
이런 부가적인 기능을 메서드에 직접 코드를 수정해서 추가하는게 어닌 원래 매서드의 코드를 수정하지 않고 부가적인 기능을 추가할 수 있게 하는 패턴이다.
특징
장점
- 기존 코드를 변경하지 않고 새로운 기능을 추가할 수 있다.
OCP - Open-Close Principle
- 기존 코드가 해야 하는 일만 유지할 수 있다.
SRP - Single Responsibility Principle
- 기능 추가 및 초기화 지연 등으로 다양하게 활용할 수 있다.
자원이 큰 객체를 늦게 초기화 하던지 혹은 로깅, 캐싱등 여러가지로 활용할 수 있다.
단점
- 코드의 복잡도가 증가한다.
Proxy 패턴 구현 예제
1. 상속을 이용한 Proxy - 인터페이스가 없는 경우
메서드 Overried를 이용해 프록시 패턴을 구현한다. - 상속성
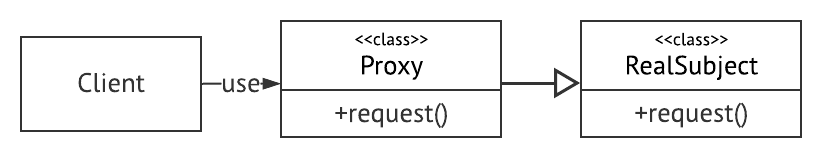
- Proxy는 RealSubject를 상속받는다.
- Proxy는 RealSubject의 메서드를 overried한다.
구현
GameService와GameService의 Proxy객체인GameServiceProxy가 있다.GameService는 start라는 매서드를 가진다.- 원래 메서드(
GameService.start())의 코드를 수정하지 않고 해당 메서드의 수행속도를 측정하고 싶다. GameServiceProxy가GameService를 상속받고 부모의start()의 수행속도를 측정한다.
// GameService(Real Subject)
public class GameService{
public void start() throws InterrubtedException{
System.out.println("Game Start!!")
}
}
// GameServiceProxy(Proxy)
public class GameServiceProxy extends GameService {
@Overried
public void start() throws InterrubtedException{
long before = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("이 자리에 오신 여러분을 진심으로 환영합니다.");
Thread.sleep(1000L);
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args){
GameService gameService = new GameServiceProxy();
gameService.start();
}
}
출력 결과
Game Start!!
1000
사용하는 이유
- Real Subject(ex.
GameService)를 고칠 수 없는 경우 상속으로 해결한다. - 인터페이스를 이용한 Proxy구조보다 비교적 단순하다.
하지만 가급적으로 인터페이스를 활용하는게 좋다.
2. 인터페이스를 이용한 Proxy
인터페이스를 이용해 프록시 패턴을 구현한다. - 다형성
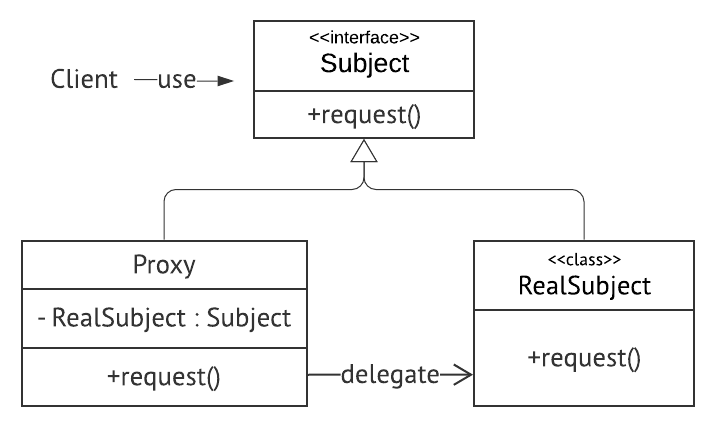
- Proxy와 RealSubject는 interface인 Subject를 구현한다.
- Proxy는 RealSubject를 가지고 있는다.
- Proxy객체는 RealSubject의 메서드를 대신 실행한다.
구현
GameService인터페이스와 그를 구현한DefaultGameService,ProxyGameService가 있다.DefaultGameService의 proxy는ProxyGameService이고 DefaultGameService를 필드로 가지고 있다.- 원래 메서드(
DefaultGameService.start())의 코드를 수정하지 않고 해당 메서드의 수행속도를 측정하고 싶다. GameServiceProxy는DefaultGameService의 메서드를 대신 실행해start()의 수행속도를 측정한다.
// DefaultGameService(RealSubject)와 ProxyGameService(Proxy)의 Subject 인터페이스
public interface GameService {
void start() throws InterruptedException;
}
// DefaultGameService(Real Subject)
public class DefaultGameService implements GameService{
@Override
public void start() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("Game Start!!!");
Thread.sleep(1000L);
}
}
// GameServiceProxy(Proxy)
public class GameServiceProxy implements GameService{
private final GameService gameService; // proxy를 적용할 RealSubject
public GameServiceProxy(GameService gameService) {
this.gameService = gameService;
}
@Override
public void start() throws InterruptedException {
long before = System.currentTimeMillis();
gameService.start();
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - before);
}
}
// Client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
GameService gameService = new GameServiceProxy(new DefaultGameService());
gameService.start();
}
}
출력 결과
Game Start!!
1000
사용하는 이유
- 사용범위가 넓다. ex. 늦은초기화
public class GameServiceProxy implements GameService{ private final GameService gameService; // proxy를 적용할 RealSubject @Override public void start() throws InterruptedException { long before = System.currentTimeMillis(); if(gameService == null){ gameService = new DefaultGameService(); // 야매지만 늦은 초기화를 수행했다. } gameService.start(); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - before); } } - 상속을 이용한 방법보다 조금 더 복잡하다.